Peritoneal Dialysis Centers in Vijayawada
What is peritoneal dialysis?
Peritoneal dialysis in Vijayawada is used to eliminate the waste products from the blood when your kidneys cannot effectively perform the job anymore. This procedure will filter the blood in various ways than the common blood-filtering procedure known as hemodialysis.
Dialysis is needed if your kidneys are no longer functioning well properly. Kidney damage advances over a number of years as an outcome of long-term conditions like:
- High Blood pressure
- Multiple cysts in the kidneys
- Diabetes
- Kidney inflammation
Types of peritoneal dialysis
There are two sorts of peritoneal dialysis:
- Continuous Ambulatory Peritoneal Dialysis (CAPD)
- Automated Peritoneal Dialysis (APD)
The essential treatment is no different for each. Nonetheless, the number of treatments and how the medicines are done make every method different.
CAPD is continuous, machine-free and done while you go about your normal activities like work or school. You do the treatment by placing around two quarts of cleansing the fluid into your belly and later draining it. This is performed by hooking up a plastic bag of cleansing the fluid to the tube in your belly. Raising the plastic bag to shoulder level makes gravity to pull the fluid into your belly. At the point when empty, the plastic bag is eliminated and discarded.
At the point when an exchange is done, the fluid is drained from your belly and thrown away. This process is done three, four or multiple times in a 24-hour duration while you are conscious during normal activities. Each exchange takes around 30 to 40 minutes. Some patients like to do their exchanges at mealtimes and at bedtime.
APD varies from CAPD in that a machine (cycler) delivers and afterward drains the cleansing fluid for you. The treatment is done at night while you sleep.
How you prepare?
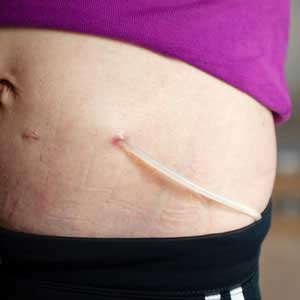
You will require an operation to place the catheter that carries the dialysate in and out of your abdomen. The insertion may be done under the local or general sedation. The tube is usually placed near your bellybutton.
After the tube is placed, your doctor will likely suggest waiting up as long as a month prior to beginning peritoneal dialysis treatments to give the catheter site time to heal.
What is the Procedure?
During peritoneal dialysis at dialysis centers in AP the dialysate flows into the abdomen and stays for a prescribed period of time for 4-6 hours. Dextrose in the dialysis aids in filtering the waste, chemicals and additional fluids in the blood from smaller blood vessels within the abdominal cavity lining.
When the dwell time is completed, the solution with the waste products taken from the blood drains into the sterile collection bag.
Results
Many factors affect how well the peritoneal dialysis works in eliminating the wastes and extra fluid from the blood. These factors include:
- Your size
- How rapidly your peritoneum filters waste
- How much dialysis solution you use?
- Number of daily exchanges
- Length of dwell times
- The concentration of sugar in the dialysis solution
Frequently asked questions on peritoneal dialysis
How does peritoneal dialysis work?
A solution called dialysate is inserted into the abdominal cavity through a catheter, and it absorbs waste products from the blood. The used dialysate is then drained and replaced with fresh solution.
What are the benefits of peritoneal dialysis?
Peritoneal dialysis can be done at home, offers more flexibility and independence than in-center hemodialysis, and can be less expensive.
How often do I need to do peritoneal dialysis?
The frequency of peritoneal dialysis depends on the type and individual needs, but it can range from every 4-6 hours for CAPD to several times a night for APD.
Can I still work or lead an active life with peritoneal dialysis?
Yes, many people with peritoneal dialysis are able to work and lead active lives, with some even engaging in high-intensity activities like sports.
Are there any complications associated with peritoneal dialysis?
Yes, potential complications include infection, inflammation, and bleeding at the catheter site, as well as fluid overload and peritonitis.
How long does it take to get used to doing peritoneal dialysis?
It typically takes a few weeks to get comfortable with the process, but many patients report feeling more comfortable within a few days.
Can I travel while doing peritoneal dialysis?
Yes, with proper planning and arrangements, it's possible to travel while doing peritoneal dialysis. However, you may need to take your equipment and supplies with you.

